Diets have greater impact on mood, mental wellness in women rather than men
02/28/2019 / By Ellaine Castillo

There is a growing body of evidence regarding the effects of diet on a person’s mental health. However, it wasn’t until recently that researchers discovered that this connection was stronger in women than in men.
A study led by Dr. Lina Begdache, an assistant professor at Binghamton University, investigated the effects of nutritional deficiency on mental well-being. To do this, they surveyed 563 participants, 52 percent of whom were women while the rest were men, regarding their dietary patterns and mental health. From this, they found that men experienced mental well-being until they become deficient in certain nutrients. Conversely, women only experienced mental well-being after following a well-balanced diet. They were also more likely to experience mental health problems when they strayed from healthy dietary patterns.
“These findings may explain the reason why women are twice more likely to be diagnosed with anxiety and depression and suffer from longer episodes, compared to men. Today’s diet is high in energy but poor in key nutrients that support brain anatomy and functionality,” said Dr. Begdache.
The team attributed these changes to a difference in brain structure between men and women. When it comes to the areas that control emotions, men tend to have a larger brain volume while women have more brain connections. These connections are easily affected by changes in diet since the different nutrients that are crucial for forming them come from a wide range of foods. On the contrary, brain volume is not easily affected by diet and it takes a longer for it to change.
Overall, the results of this study suggest that diet has great potential in treating mental health problems, especially in women.
Foods that help improve mental health
When it comes to improving mental health, certain diets might work differently for different people. So, a better approach would be knowing what specific foods are beneficial for mental well-being. The following are some examples of nutrient-dense foods that you should consider including in your diet:
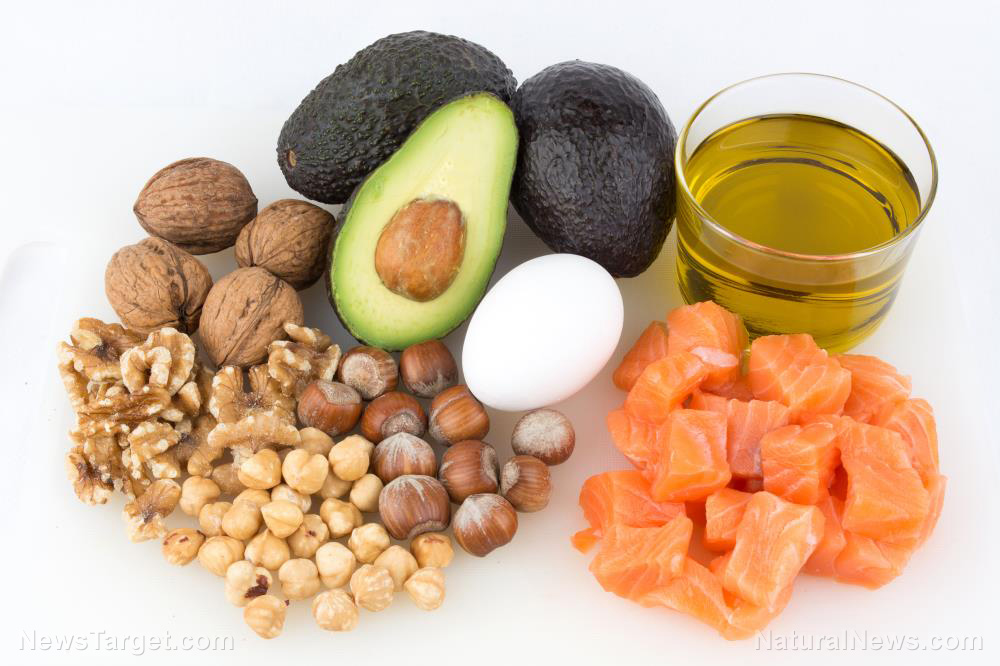
- Fatty fish — Studies have shown that increasing your intake of fatty fish can improve symptoms of schizophrenia, depression, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, and other mental disorders. This effect is attributed to a type of polyunsaturated fatty acid known as omega-3. This nutrient boosts the production of feel-good chemicals like dopamine and serotonin in order to improve mood. (Related: High intake of omega-3 found to significantly reduce depression in people with cardiac problems.)
- Whole grains — For the brain to function properly, it requires adequate amounts of glucose, which come from carbohydrates. However, not all carbohydrates are good for the brain. Simple carbohydrates cause spikes in blood sugar and induce effects on the brain that are similar to drugs of abuse. This is why complex carbohydrates, such as those found in whole grains, are preferred.
- Lean protein — Lean proteins from fish, turkey, chicken, eggs, and beans are good for the brain. These serve as sources of tryptophan, an essential component for the production of serotonin. Many people who have insufficient levels of this brain chemical suffer from mental health problems like depression and anxiety.
- Leafy greens — The highly nutritious leafy greens, which include spinach, romaine, and broccoli, are an important part of a healthy diet. These contain high levels of folate and other B vitamins that help prevent depression, fatigue, and insomnia. Aside from this, broccoli contains selenium, an important mineral for hormone production, immunity, and reproduction.
Read more news articles on how you can improve your mental well-being by visiting MindBodyScience.news.
Sources include:
Tagged Under: Anxiety, brain health, mental wellness, mood, nutrients